What does the engine sensor include?
The main engine sensors (9) of the engine include:
Air flow engine sensor (MAF), throttle position engine sensor (TPS), accelerator pedal position engine sensor (ETPS), intake air temperature engine sensor (MAT), coolant temperature engine sensor (ECT), camshaft position engine sensor ( CMP), crankshaft position engine sensor (CKP), oxygen engine sensor, knock engine sensor (KS).
Among them, the main signal for controlling the fuel injection quantity is the air flow engine sensor and the crankshaft position engine sensor, and the correction signal is the oxygen engine sensor. Additional signals are coolant temperature engine sensor and intake air temperature engine sensor.
The main signal that controls the ignition signal is the crankshaft and camshaft position engine sensor, the correction signal is the knocking engine sensor, and the additional signal is the coolant temperature engine sensor.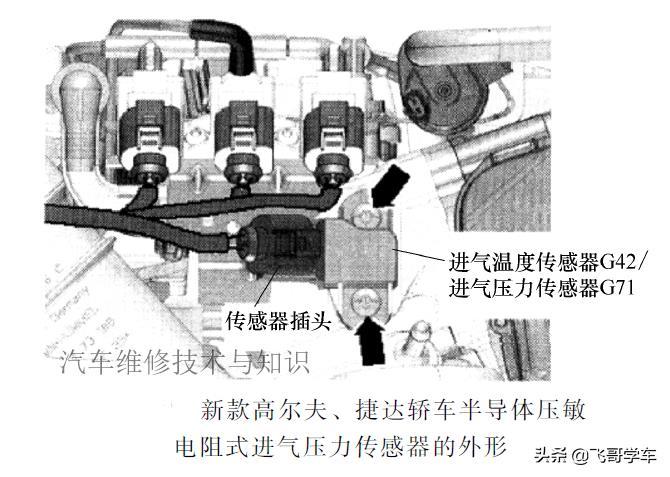
Expansion information:
An engine is a machine that can convert other forms of energy into mechanical energy, including internal combustion engines (gasoline engines, etc.), external combustion engines (Stirling engines, steam engines, etc.), electric motors, etc. For example, internal combustion engines usually convert chemical energy into mechanical energy. The engine applies to both the power generating unit and the entire machine including the power unit (eg gasoline engine, aircraft engine). The engine was first born in the United Kingdom, so the concept of the engine is also derived from English, and its original meaning refers to the kind of "mechanical device that generates power".
The body is the skeleton that constitutes the engine, and is the installation base of the various mechanisms and systems of the engine. All the main parts and accessories of the engine are installed inside and outside it, and bear various loads. Therefore, the body must have sufficient strength and rigidity. The body group is mainly composed of cylinder block, cylinder liner, cylinder head and cylinder gasket and other parts.
How many engine sensors does the engine have
There are the following engine sensors:
1. The crankshaft engine sensor accurately calculates the position of the crankshaft, which is used for the calculation of fuel injection timing, fuel injection quantity and rotational speed.
2. When the camshaft engine sensor judges the cylinder and the crankshaft engine sensor fails, it is used to go home lame (temporary operation).
3. The intake air temperature engine sensor measures the intake air temperature, corrects the fuel injection quantity and fuel injection timing, and protects against overheating.
4. The supercharging pressure engine sensor monitors the intake air pressure, calculates the intake air volume together with the intake air temperature, and integrates it with the intake air temperature.
5. The cooling water temperature engine sensor measures the cooling water temperature, which is used for cold start, target idle speed calculation, etc., and is also used to correct the fuel injection advance angle and overheat protection.
6. The common rail pressure engine sensor measures the fuel pressure in the common rail pipe to ensure stable oil pressure control.
7. The throttle position engine sensor sends the driver's intention to the controller ECU.
8. The vehicle speed engine sensor provides the vehicle speed signal to the ECU for vehicle drive control, which is provided by the vehicle.
9. The atmospheric pressure engine sensor is used to correct the fuel injection control parameters at different altitudes and is integrated in the ECU.
There are also cylinder pressure engine sensor, knocking engine sensor, and some engine sensors for monitoring post-processing CH and NO emissions in the future, etc.






